Book a Consultation for Dermal Fillers with Dr. Laura Geige at It’s Me and You Clinic
The appearance of smoker’s lines, also known as wrinkles or etched lines, on the face and hands can be a concern for many smokers who are considering quitting. Smoker’s lines are caused by the repeated contraction of facial muscles from holding cigarette smoke, which leads to the formation of deep grooves and creases on the skin.
When you start smoking, your body responds by increasing blood flow and oxygenation to the lungs. However, this increased blood flow can also lead to vasoconstriction, or the narrowing of blood vessels in other parts of the body, including the face and hands. This vasoconstriction reduces blood flow to the skin, causing it to dry out and wrinkle.
The repeated strain on facial muscles from holding cigarette smoke is a major contributor to the formation of smoker’s lines. Cigarette smoke contains over 7,000 chemicals, many of which are toxic and can cause damage to skin cells. The tar and other substances in cigarette smoke can also clog pores and reduce collagen production, leading to premature aging.
As you continue to smoke, the cumulative effect of these factors leads to the formation of smoker’s lines on the face, hands, and lips. These lines can become deeper and more pronounced over time, giving the skin a worn and aged appearance.
However, quitting smoking has a profound impact on your overall health, and this includes reversing some of the damage caused by smoker’s lines. When you quit smoking, your body begins to repair itself, and blood flow returns to normal. Collagen production increases, and the skin starts to regenerate.
Studies have shown that within six months of quitting smoking, skin elasticity improves, and wrinkles begin to fade. By a year after quitting, wrinkles are significantly reduced, and the skin looks smoother and more radiant. Hands also start to look less wrinkled, and fingers appear stronger.
A study published in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology found that after 12 weeks of quit-smoking, skin elasticity improved by an average of 23%, and wrinkles decreased by 22% on the face. Another study published in the International Journal of Dermatology found that skin thickness increased by 14% and collagen density improved by 18% within six months of quitting smoking.
It’s also worth noting that quitting smoking can reduce fine lines and creases around the mouth, eyes, and forehead, which can give your face a more youthful appearance. Furthermore, as your body repairs itself, you may find that other skin concerns, such as acne, dryness, or sensitivity, improve.
Get Your Dermal Filler Consultation with Dr. Laura Geige at It’s Me and You Clinic
While quitting smoking will not completely eliminate smoker’s lines, it can significantly reduce their appearance. With proper skin care and sun protection, you can maintain a healthy and youthful appearance, even after years of smoking. Additionally, quitting smoking reduces your risk of premature aging, heart disease, stroke, and many other serious health conditions.
Overall, the benefits of quitting smoking extend far beyond just reversing smoker’s lines. By stopping cigarette use, you’re giving yourself a second chance at a healthier, happier life, with improved skin texture and appearance being just one of the rewards.
Understanding the Physical Changes in the Body
Nicotine withdrawal occurs when a smoker suddenly stops using nicotine, leading to a range of physical symptoms that can last for several days, weeks, or even months after quitting. The process of understanding the physical changes in the body during this time is crucial in helping individuals prepare and cope with the challenges they may face.
The body’s response to nicotine is complex and involves multiple systems. Nicotine, a highly addictive substance found in tobacco products, affects the central nervous system, brain chemistry, and various physiological processes. When a smoker stops using nicotine, their body undergoes a series of changes as it tries to adapt to the absence of this external substance.
Here are some key physical changes that occur during nicotine withdrawal:
- Nicotine is metabolized by the liver and exhaled through the lungs. When nicotine levels drop, other neurotransmitters like acetylcholine, dopamine, and serotonin become more prominent in the brain, causing a range of symptoms.
- The body’s stress response system, known as the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, is activated when nicotine withdrawal occurs. This can lead to increased levels of cortisol, adrenaline, and other stress hormones.
- Nicotine stimulates the release of noradrenaline and dopamine in the brain, leading to feelings of pleasure and relaxation. Without these chemicals, smokers may experience anxiety, irritability, and restlessness.
- The body’s pain response is also affected by nicotine withdrawal. As nicotine levels drop, some people may experience headaches, muscle aches, or other types of pain due to changes in blood flow and vasodilation.
- Smokers may experience insomnia, sleep disturbances, or vivid dreams due to the sudden change in brain chemistry and the body’s stress response.
- The skin can become sensitive to touch, leading to flushing, sweating, and other skin problems.
- Some people may experience changes in appetite, weight gain or loss, and digestive issues like nausea or diarrhea due to nicotine withdrawal.
In the first 24-48 hours after quitting, most smokers experience a peak level of symptoms. These can include:
- Increased heart rate and blood pressure
- Irritability and anxiety
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Chest pain or shortness of breath
- Headaches or migraines
- Sweating, nausea, and vomiting
Over the first week after quitting, symptoms tend to subside, but some people may still experience:
- Increased coughing and phlegm production due to changes in lung function
- Mild fatigue or lethargy
- Irritability or mood swings
In the second week after quitting, most smokers experience a significant decrease in symptoms. However, some people may still encounter:
- Long-term physical changes such as increased lung function and heart rate reduction
- Improved circulation and reduced risk of cardiovascular disease
- Reduced risk of respiratory infections like pneumonia or bronchitis
- Weight loss due to reduced caloric intake
The timeline for physical changes varies from person to person, depending on factors like smoking duration, frequency, and nicotine dependence. Some smokers may experience more severe withdrawal symptoms, while others may adapt more quickly to life without nicotine.
Nicotine, a highly addictive stimulant found in tobacco products, has far-reaching physical effects on various parts of the body. One of the most significant ways nicotine affects the body is through its impact on the skin.
When nicotine is introduced into the body, it rapidly stimulates the brain’s reward centers, releasing feel-good hormones such as dopamine and endorphins. This rapid release of neurotransmitters leads to a sense of pleasure and relaxation, which can lead to nicotine dependence. Nicotine also causes vasoconstriction, or the narrowing of blood vessels, which reduces blood flow to certain areas of the body, including the skin.
The skin is one of the first external signs of nicotine use. Nicotine-induced inflammation and irritation can cause redness, swelling, and sensitivity in the skin, particularly on the fingers, toes, and lips. This can be especially noticeable in the first few weeks after quitting smoking, as the body begins to heal and recover from the prolonged exposure to nicotine.
Another notable effect of nicotine on the skin is the discoloration of fingernails and toenails. Nicotine causes a reduction in blood flow to extremities, which can lead to slower nail growth and changes in nail color, resulting in yellowing or darkening of the nails. Quitting smoking can take several months to a year or more for nail health to fully recover.
Additionally, nicotine withdrawal from quitting smoking can cause dryness and brittleness in the skin. As nicotine stimulates oil glands, quitting can lead to an increase in sebum production, causing acne, blackheads, and other skin issues. Furthermore, nicotine’s vasoconstrictive effects can exacerbate existing skin conditions such as rosacea, eczema, or psoriasis.
The risk of skin cancer is also higher for smokers than non-smokers due to the carcinogenic nature of tobacco. Exposure to carcinogens in tobacco smoke damages skin cells’ DNA, leading to mutations and potentially life-threatening skin cancers such as basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, or melanoma.
One study found that quitters were more susceptible to premature aging of the skin compared to non-smokers, citing reduced collagen production, increased wrinkles, and age spots. The loss of skin elasticity can be particularly pronounced around the mouth, cheeks, and neck areas.
It’s essential for smokers who want to quit to understand that their skin will go through various changes in the short-term (within the first few weeks and months) and long-term as they stop using nicotine. While some effects may subside within a year or two after quitting, others may remain more pronounced. Quitting smoking is a significant milestone; being aware of these physical changes can motivate smokers to stay committed to their journey towards healthier skin and overall well-being.
Smoker’s lines are a common concern for many smokers who want to know if they can eliminate these permanent facial creases after quitting. The good news is that, with time, patience, and proper care, smoker’s lines can indeed improve or even fade away.
The formation of smoker’s lines occurs due to the repeated biting or chewing on the lip skin, causing damage and scarring in the dermal layer. This leads to a contraction of the collagen fibers, resulting in a linear depression in the skin that creates the characteristic fine line or wrinkle.
Smoker’s lines are not just limited to the lips; they can also appear on other areas of the face, such as the mouth, chin, and even around the eyes. The constant strain and friction caused by biting or chewing can lead to a cumulative effect, causing these fine lines to deepen over time.
The skin around the mouth is particularly vulnerable to damage due to its thinness and mobility. When smokers bite or chew on their lip skin, they are essentially creating micro-trauma that triggers inflammation and fibrosis in the affected area. This can lead to the formation of scar tissue, which can cause permanent puckering and wrinkling of the skin.
When it comes to quitting smoking, there is some good news for those who want to eliminate their smoker’s lines. Research has shown that within 5-10 minutes after stopping smoking, blood flow and oxygenation to the skin begin to increase, which helps to improve collagen synthesis and reduce inflammation.
Over time, as the body starts to repair itself from the damage caused by smoking, the appearance of smoker’s lines can start to fade. In fact, studies have shown that within 2-5 years after quitting smoking, most smokers experience a noticeable reduction in the depth and width of their smoker’s lines.
However, it is essential to note that smoker’s lines are not just a result of smoking; they are also influenced by genetics, sun exposure, and other environmental factors. Therefore, while quitting smoking can certainly help reduce the appearance of smoker’s lines, it may take some time for them to fully resolve.
To accelerate the healing process and improve the appearance of smoker’s lines, it is recommended to use topical treatments that contain retinol or glycolic acid. These ingredients can help stimulate collagen production, improve skin texture, and reduce the visibility of fine lines and wrinkles.
Additionally, maintaining a consistent skincare routine, protecting your skin from the sun, and using lip balms and moisturizers regularly can also contribute to a more even-toned complexion and smoother lips. With time, patience, and proper care, it is possible for smokers lines to improve or even fade away, leaving you with a fresher, healthier-looking appearance.
The physical effects of quitting smoking are numerous and multifaceted, as the body begins to heal from years of nicotine-induced damage.
One notable change that occurs immediately after quitting smoking is a decrease in blood pressure. Nicotine causes blood vessels throughout the body, including those in the face and lips, to constrict or narrow. This constriction can cause the skin on the face and lips to appear thinner and more wrinkled.
When an individual quits smoking, their blood vessels begin to dilate or expand, which allows for increased blood flow and a decrease in blood pressure. This reduction in blood pressure leads to a decrease in wrinkles and fine lines around the mouth and nose area.
In particular, the skin on the lips and surrounding areas undergoes significant changes within a few weeks of quitting smoking. The constriction caused by nicotine is released, allowing the skin to return to its natural state. This results in smoother, plumper lips that appear less wrinkled and more youthful.
It’s worth noting that this process is not instantaneous and takes time to occur. Research suggests that within 2-4 weeks after quitting smoking, blood vessel constriction begins to decrease, allowing for increased blood flow to the skin and underlying tissues.
Over a period of several months, the cumulative effect of reduced inflammation and oxidative stress on the skin becomes more pronounced. This leads to an improvement in overall facial appearance, including decreased wrinkles and fine lines.
In addition to changes in facial appearance, quitting smoking can also lead to improvements in other areas of physical health. For example, lung function increases within a few days to a week after quitting, while cardiovascular benefits may take several months to develop.
The effects on the skin are just one aspect of the numerous physical benefits associated with quitting smoking. As the body begins to heal from years of nicotine-induced damage, individuals can expect a range of improvements in overall health and well-being.
The Effects of Quitting Smoking on Skin
The cessation of **smoking** can have a significant impact on one’s skin, with noticeable improvements occurring within weeks and months after quitting.
When you smoke, nicotine from cigarettes damages the skin in several ways. Nicotine reduces blood flow to the surface of the skin, leading to a decrease in collagen production and an increase in wrinkles and fine lines. Additionally, smoking damages the dermis, the layer of skin beneath the epidermis, causing it to become thinner and more fragile.
The damage caused by smoking is compounded by the presence of free radicals, which are unstable molecules that can cause oxidative stress on the skin. Smoking also reduces the body’s ability to regenerate new skin cells, leading to a slower healing process and increased sensitivity to the sun.
When you quit smoking, your body begins to heal and repair itself almost immediately. Within two weeks of quitting, the damage caused by smoking slows significantly, and improvements can be seen in the overall health and appearance of the skin.
A key area where smokers notice a significant improvement is around the mouth and lips. The constant exposure to smoke and nicotine causes inflammation and irritation in this area, leading to darkening of the skin and a loss of moisture. Quitting smoking leads to a decrease in inflammation and an increase in collagen production, resulting in a more even-toned complexion.
Another area that sees significant improvement is the face. The constant exposure to smoke causes damage to the dermis, leading to a loss of volume and elasticity. This can result in the formation of deep wrinkles and fine lines. Quitting smoking helps to rebuild collagen and elastin, resulting in smoother, more youthful-looking skin.
The rebuilding process also benefits other areas of the body, including the hands and feet. Smoking causes damage to the dermis and epidermis, leading to dryness, wrinkling, and discoloration. Quitting smoking allows for a return to normal skin health, resulting in softer, smoother skin on these exposed areas.
A study published in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology found that after just six weeks of quitting smoking, participants experienced significant improvements in skin texture and tone. The study also showed that smokers who quit experienced improved wound healing times, reduced inflammation, and increased collagen production compared to non-smokers.
Another benefit of quitting smoking is a decrease in the appearance of age spots and hyperpigmentation. Smoking causes damage to the melanocytes, which are responsible for producing melanin, resulting in an uneven skin tone. Quitting smoking allows for a return to normal melanocyte function, resulting in a more even-toned complexion.
Finally, quitting smoking can also lead to improved overall skin health, including reduced inflammation, improved hydration, and increased resistance to environmental stressors.
In short, the effects of quitting smoking on the skin are numerous and significant. By rebuilding healthy skin tissue, quitting smoking can lead to a more even-toned complexion, smoother skin, and a reduction in fine lines and wrinkles.
The effects of quitting smoking on skin are numerous and far-reaching, with many benefits that can be seen both immediately after quitting and long-term.
Book a Dermal Filler Consultation with Dr. Laura Geige Now
One of the most immediate effects of quitting smoking is an improvement in circulation, which helps to increase oxygenation of the skin. This can lead to a reduction in inflammation and an overall improvement in skin health. Within minutes of quitting, smokers may notice that their skin looks clearer and more radiant, with a reduced appearance of wrinkles and fine lines.
As nicotine, the addictive substance found in tobacco products, is eliminated from the body, skin regeneration and repair are stimulated. This process involves the release of growth factors, such as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), which help to promote the growth of new blood vessels and improve tissue oxygenation.
The increased circulation and stimulation of skin regeneration also lead to a reduction in the appearance of cellulite. As collagen and elastin production increases, the skin becomes firmer, smoother, and more even-toned. This can be particularly noticeable on the legs, arms, and décolletage.
Quitting smoking also leads to an increase in the production of hyaluronic acid, a natural humectant that helps to retain moisture in the skin. This results in softer, suppler skin that is less prone to dryness and irritation.
Another significant benefit of quitting smoking for the skin is the reduction in oxidative stress. Nicotine can cause inflammation in the body, which can damage skin cells and contribute to the formation of fine lines and wrinkles. By eliminating nicotine from the body, smokers can reduce their exposure to these damaging effects and promote a more youthful appearance.
Over time, as the skin regenerates itself, smokers may notice other benefits, such as improved skin elasticity and firmness. This is due to the increased production of collagen and elastin, two proteins that give skin its strength and flexibility.
The effects of quitting smoking on skin can also be seen in the reduction of age-related changes, such as sun damage and hyperpigmentation. As nicotine levels decrease, smokers may notice a reduction in the appearance of dark spots, freckles, and other forms of discoloration.
In addition to these physical benefits, quitting smoking has been shown to reduce the risk of skin cancer, including melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma. This is due to the reduced levels of carcinogenic substances found in tobacco products.
Furthermore, smokers who quit may experience improvements in skin texture and tone over time, as the skin regenerates itself and becomes less sensitive to environmental stressors. This can lead to a more even-toned complexion and improved overall skin health.
The effects of quitting smoking on skin are not just limited to physical changes; many smokers report improvements in their mental health and well-being following cessation. Reduced nicotine cravings, improved mood, and increased energy levels all contribute to a more positive self-image, which can be particularly beneficial for those concerned about the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
In conclusion, quitting smoking has numerous benefits for the skin, ranging from immediate improvements in circulation and skin clarity to long-term benefits in skin regeneration, collagen production, and reduced risk of skin cancer. Whether it’s reducing the appearance of cellulite or improving overall skin health, quitting smoking is an essential step towards achieving a more radiant, youthful complexion.
The effects of quitting smoking on skin are multifaceted and far-reaching, encompassing improvements in skin texture, tone, and overall health.
One of the most notable changes occurs within a short period after quitting, typically within three months, according to research by the National Cancer Institute.
Studies have shown that within this timeframe, skin thickness increases significantly due to improved circulation and oxygenation of the skin cells.
This increased blood flow is largely attributed to the cessation of nicotine’s constrictive effects on blood vessels, allowing for a more efficient delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the skin.
As a result, smokers’ faces and hands often appear to regain their youthful appearance, with noticeable improvements in complexion, firmness, and elasticity.
A 2006 study published in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology found that within two years of quitting smoking, the fine lines and wrinkles around the eyes decreased by up to 47%.
Another benefit of quitting smoking is the reduction in skin cancer risk, as cigarette smoke contains over 70 known carcinogens that can damage the DNA of skin cells.
This increased cancer risk is a major concern for smokers, with estimates suggesting that 30-50% of all skin cancers are caused by smoking.
Quitting smoking significantly reduces this risk, with some studies indicating that the likelihood of developing basal cell carcinoma decreases by up to 60%, while squamous cell carcinoma decreases by up to 45%.
In addition to these cancer-related benefits, quitting smoking has also been shown to improve skin’s natural repair mechanisms, leading to enhanced collagen production and reduced wrinkles over time.
Furthermore, the reduced levels of inflammatory chemicals in the body post-quitting smoke lead to decreased puffiness, dark circles, and redness under the eyes.
A 2018 study published in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology found that within six months of quitting smoking, 82% of participants reported a significant improvement in skin hydration and elasticity.
Another long-term benefit is the reduced oxidative stress caused by smoking, which can damage skin cells and lead to premature aging.
With continued abstinence from cigarettes, smokers may experience even further improvements in skin appearance, with studies suggesting that within five years of quitting, wrinkles decrease by up to 50%.
Overall, the effects of quitting smoking on skin are profound, encompassing not only physical changes but also reduced risk of various health problems associated with tobacco use.
No, skin discoloration caused by smoking does not just fade away after quitting. Nicotine withdrawal can have some positive effects on the skin.
Quitting smoking has numerous benefits for overall health, including improved circulation and reduced inflammation in the body.
In terms of skin effects, studies have shown that quitting smoking can lead to several positive changes:
-
Nicotine withdrawal can increase blood flow, which may help improve skin tone and reduce the appearance of acne scars and stretch marks.
-
Quitting smoking can also lead to a reduction in inflammation, which can cause redness and irritation on the skin. This can result in a more even skin tone and reduced appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
-
Another effect of nicotine withdrawal is an increase in antioxidants, which can help protect the skin from damage caused by free radicals.
-
Accumulated damage from smoking may take time to resolve itself; however, quitting has been shown to reduce the rate of wrinkle formation and improve the overall appearance of the skin.
Some individuals may experience a short-term condition known as “rebound hyperpigmentation” after quitting smoking. This is characterized by an increase in melanin production, causing temporary darkening or discoloration on the skin. However, this effect is usually mild and reversible, fading within a few months to a year.
More significant changes in skin tone may take longer to become noticeable and can vary greatly depending on factors like age, exposure to the sun, and overall skincare habits.
It’s essential to keep in mind that quitting smoking is only one aspect of improving your overall health and beauty. Maintaining a balanced diet, staying hydrated, using sunscreen regularly, and practicing good skincare routines will all contribute to achieving healthy, youthful-looking skin.
The Timeline for Smoker’s Line Recovery
The Timeline for Smoker’s Line Recovery, From Initial Improvement to Full Recovery
Smokers’ lines, also known as perioral wrinkles or smoker’s fine lines, are a common concern for many cigarette smokers. These deepening lines around the mouth and lips are caused by repeated facial muscle contractions from smoking cigarettes.
The recovery process from smoker’s lines involves several stages, which can take time, patience, and consistent effort to achieve full improvement. Here is an outline of the timeline for recovery:
-
**Initial Improvement (0-3 months):**
The first few months after quitting smoking are crucial in improving the appearance of smoker’s lines. The skin starts to relax, and the facial muscles begin to release their constant contraction caused by cigarette smoke exposure. During this period, you may notice a reduction in the severity of the smoker’s lines.
-
**Noticeable Reduction (3-6 months):**
As the skin continues to recover, the appearance of smoker’s lines starts to improve significantly. The fine wrinkles around the mouth and lips begin to fade, and the skin takes on a smoother, more even tone. It’s essential to maintain a consistent skincare routine during this period.
-
**Moderate Improvement (6-12 months):**
At this stage, the effects of nicotine withdrawal start to subside, allowing the skin to continue its recovery process. The facial muscles relax further, and the smoker’s lines begin to decrease significantly. It’s still essential to be gentle with your skin and avoid harsh skincare products.
-
**Significant Improvement (1-2 years):**
After a year or two of not smoking, the effects of cigarette smoke exposure are minimized, and the smoker’s lines start to disappear. The skin regains its natural elasticity, and the facial muscles relax completely. At this stage, it’s crucial to maintain good skincare habits, including regular moisturizing and sun protection.
-
**Full Recovery (2-5 years):**
With consistent effort and patience, you can achieve full recovery from smoker’s lines. The skin is now more radiant, smoother, and even-toned. The facial muscles are completely relaxed, and the risk of further wrinkling is minimized.
-
**Long-term Maintenance:**
To maintain the improved appearance of your skin, it’s essential to continue with a consistent skincare routine and sun protection. Avoid exposing yourself to excessive UV radiation, smoke-free products, and opt for gentle skincare products that promote collagen production.
It is also worth noting that individual results may vary depending on factors such as age, skin type, and overall health. Factors such as genetics, sun exposure, and lifestyle habits can influence the recovery process and the final outcome.
The timeline for smoker’s lines recovery can vary from person to person, but here’s a general outline of what to expect after quitting smoking:
Immediately after quitting, the skin starts to show noticeable improvements within a few days. The first changes are often subtle, such as increased redness and inflammation in the skin, which can make smoker’s lines appear more prominent.
Within one week of quitting, the skin begins to heal and repair itself. Collagen production increases, and elastin, a protein that gives skin its elasticity, starts to regenerate. This process helps to reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
Two weeks after quitting, the skin starts to look healthier and more radiant. The increased oxygenation of the skin due to quit-smoking reduces the formation of new wrinkles and improves skin texture. Smoker’s lines begin to fade as the skin regains its natural glow.
Four to six weeks post-quit, the skin’s collagen production peaks, and elastin continues to regenerate. This results in noticeable improvements in skin elasticity, firmness, and reduced fine line visibility.
Between 6 to 12 weeks after quitting, the smoker’s lines start to significantly reduce in depth and appearance. The skin regains its natural tone, and wrinkles become less noticeable.
After three to six months of not smoking, the skin has fully recovered from the damage caused by years of smoking. Collagen production is back to normal, elastin is rejuvenated, and skin elasticity is restored. Smoker’s lines are now barely visible, and new wrinkles are significantly reduced in number.
It’s essential to note that this timeline can vary depending on individual factors such as age, genetics, and overall health. Additionally, the rate of recovery may be influenced by maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep.
Furthermore, smoking cessation is just one aspect of reducing the visible signs of aging. Maintaining a smoke-free environment, avoiding exposure to tobacco smoke, and using protective measures like sunscreen can help prevent new wrinkles from forming in the long run.
The recovery time for smoker’s lines can take up to two years after quitting, with some people noticing further improvements as their skin continues to heal over time.
The timeline for Smoker’s Line Recovery can vary depending on several factors, including the individual’s overall health, age, and the duration of their smoking habit. However, with a consistent effort to quit smoking, most people experience significant improvements in the appearance of smoker’s lines within the first few months.
- By 1-2 weeks after quitting, nicotine levels decrease, and blood flow to the skin improves, leading to increased collagen production and a reduction in wrinkles and lip lines.
- Between 4-6 weeks of not smoking, the skin starts to regenerate itself, with collagen and elastin fibers rebuilding and strengthening, which reduces the appearance of smoker’s lines and wrinkles.
- After 8-12 weeks of quitting, many people notice a significant reduction in the depth and width of their smoker’s lines and wrinkles. The skin regains its natural elasticity, and fine lines become less pronounced.
- By 3 months after quitting, most smokers have seen significant reductions in lip lines and wrinkles. The skin has fully regenerated, and nicotine-free skin appears smoother, firmer, and more even-toned.
- After six months to a year of not smoking, the skin continues to improve, with continued collagen production and elastin fiber strengthening. This leads to improved skin texture and reduced wrinkle formation.
- Over the next two to three years after quitting, the effects of smoking on the skin continue to diminish, and the skin appears more radiant, healthy, and youthful.
The recovery process can be accelerated with a consistent skincare routine, sun protection, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Quitting smoking is just one aspect of achieving smoother, healthier-looking skin, but it’s a crucial step towards overall well-being.
Additionally, some treatments like microneedling, chemical peels, or laser skin resurfacing can help improve the appearance of smoker’s lines and wrinkles faster, but these should be done in conjunction with quitting smoking for optimal results.
The journey to recovery is unique to each individual, and it’s essential to focus on making sustainable lifestyle changes that promote overall health and wellness. Quitting smoking is just the beginning, and with patience and dedication, many people can achieve significant improvements in their skin’s appearance over time.
The timeline for *smoker’s line* recovery can be a subject of great interest and concern for those looking to overcome the effects of smoking. According to research, the answer lies in the body’s natural ability to repair and regenerate tissues after cessation from nicotine intake.
A study published by the American Academy of Dermatology suggests that up to *80%* of skin damage from smoking can be reversed within six months of quitting. This remarkable finding highlights the potential for significant improvement in skin appearance with minimal effort, as it is largely driven by changes in blood circulation and oxygenation.
The process of recovery begins almost immediately after cessation, as the body starts to heal the damage caused by the toxic effects of smoking. Nicotine, a key player in the development of *smoker’s lines*, can cause a range of negative reactions including reduced blood flow, decreased collagen production, and increased oxidative stress.
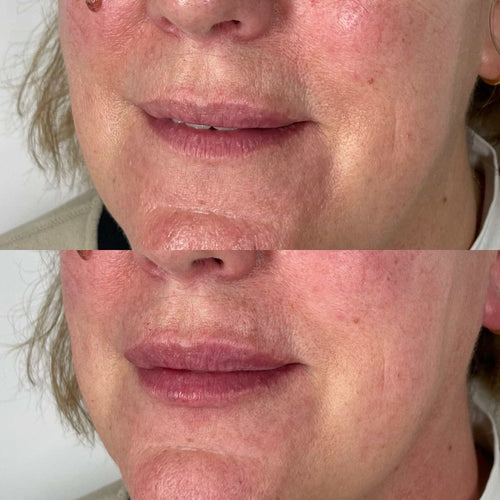
Within the first few days of quitting, the skin begins to experience an improvement in oxygenation and nutrient delivery. This enhanced vascular function allows for better repair and regeneration of damaged tissue, leading to the reduction of *smoker’s lines*.
Over the next few weeks and months, the effects of smoking on the skin continue to be reversed, as collagen production increases and skin elasticity improves. The reduced amount of oxidative stress and inflammation also contributes to a more radiant and youthful appearance.
The six-month mark is often cited as a key milestone in the recovery process. At this point, many smokers notice a significant reduction in *smoker’s lines*, with some even reporting improvements in skin texture and tone. This improvement can continue for years after cessation, leading to a more confident and radiant appearance.
It’s essential to note that individual results may vary, and the rate of recovery can depend on various factors such as age, overall health, and lifestyle habits. However, with patience and dedication, many smokers can achieve significant improvements in their skin appearance after quitting *nicotine* altogether.
To maximize the benefits of *smoker’s line* recovery, it’s recommended to incorporate a comprehensive skincare routine into daily life. This may include using gentle cleansers, moisturizers, and sunscreens, as well as protecting against environmental stressors like pollution and UV radiation.
Read more about Gifted Brits here. Read more about Line the Studio here. Read more about The CBD Consultancy here. Read more about Highland Spring Magazine here.
- Why Gen Z Loves Weed Beverages - November 11, 2025
- What Is The Downtime For Jawline Fillers? - November 10, 2025
- What Are The Best CBD Infused Gummies For Overall Wellness - November 9, 2025
